Dental implants have revolutionized the way we approach oral health and aesthetics. They are a beacon of hope for those who have lost teeth, offering a solution that not only looks natural but also functions effectively.
In this article, we delve into the intricacies of dental implants, exploring their types, materials, and aesthetic considerations.
Our journey will provide insights into the technology behind these dental marvels and their transformative impact.
The Anatomy of a Dental Implant
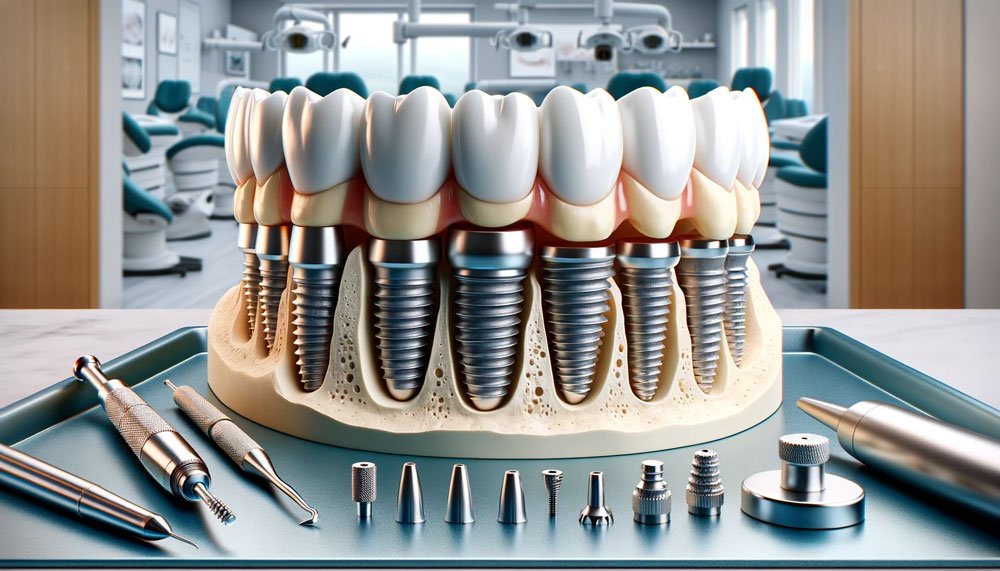
Components of an Implant
A dental implant consists of three key parts: the implant itself, the abutment, and the crown.
The implant, typically made of titanium, is a small post-like structure that is surgically inserted into the jawbone, acting as a root for the artificial tooth.
The abutment sits atop the implant, serving as a connector that holds the crown – the visible part of the implant designed to mimic your natural teeth.
Visual Representation
To better understand, imagine an infographic depicting these three components in detail. The implant, resembling a screw, anchors into the jawbone.
The abutment, almost like a small cuff, links the implant to the crown, which is artistically crafted to replicate the look of natural teeth.
Types of Dental Implants
Endosteal Implants
These are the most common type of implants. They are shaped like small screws and are placed directly into the jawbone. Their appearance, once the process is complete, is indistinguishable from natural teeth.
Subperiosteal Implants
These implants rest on top of the jawbone but under the gum. They are used when the patient does not have enough healthy jawbone for an endosteal implant. They have a unique framework that supports multiple teeth.
Visuals
Pictures of both types can help in visualizing the differences. Endosteal implants appear more streamlined, while subperiosteal implants have a more complex structure.
Material Matters
Titanium Implants
Titanium, known for its strength and compatibility with body tissues, is the traditional material for implants. Its appearance is metallic, but it’s hidden beneath the gum line and the crown.
Zirconia Implants
An alternative to titanium, zirconia implants are white, offering a more natural appearance, especially for patients with thin gums.
Comparison Chart
A chart can illustrate the properties of each material, such as durability, aesthetic appeal, and biocompatibility.
Aesthetic Considerations
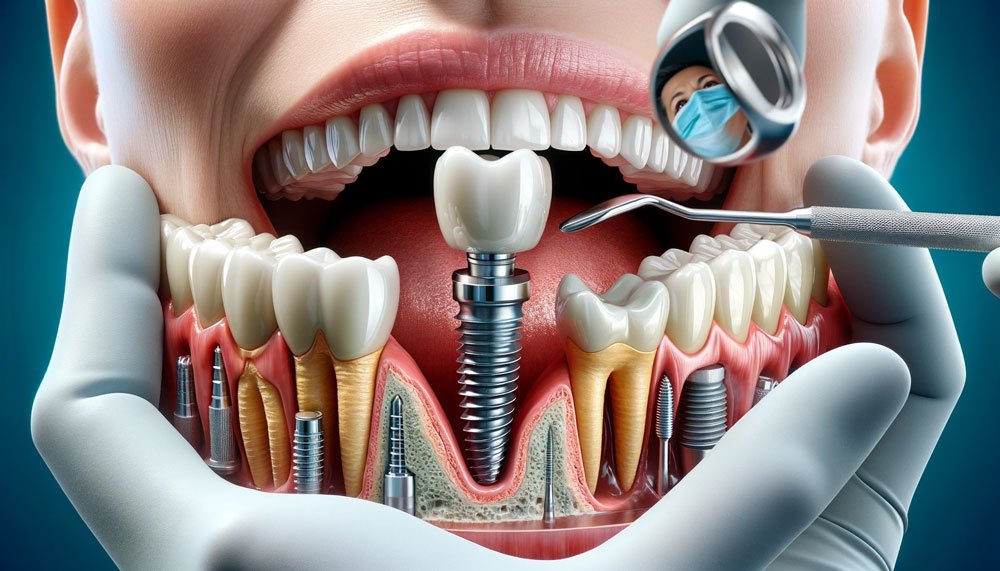
Customization
Dental implants are designed to blend seamlessly with your natural teeth. The crowns can be color-matched and shaped according to the surrounding teeth, ensuring they look as natural as possible.
Before and After Images
Visual transformations showcased through before-and-after images can be striking. They not only demonstrate the aesthetic improvement but also highlight the restorative benefits.
Technological Advances in Implant Design
Innovative Designs
Recent advancements include implants with better osseointegration (bonding with the bone) and micro-textured surfaces for quicker healing. These may be visualized through 3D models or animations, showing their intricate designs.
Functional Benefits
These designs enhance the stability and longevity of implants, improving overall oral health.
Additional Insights or Information
Patterns and Trends
The trend is moving towards more biocompatible materials and designs that promote faster healing and better integration with the jawbone.
Honorable Mentions
Other methods like bridges or dentures, while not the focus of this article, also play a significant role in dental restoration.
Conclusion
Dental implants are more than just a cosmetic fix; they are a testament to the incredible advances in dental technology.
From their intricate design to the materials used, each aspect plays a crucial role in their functionality and appearance.
Understanding these elements helps us appreciate the complexity and effectiveness of dental implants as a solution for tooth loss.
As technology progresses, we can expect even more refined and efficient implants continuing to transform smiles worldwide.
